I. Introduction
As the world transitions towards a more sustainable future, electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly gaining popularity. With their zero tailpipe emissions and lower environmental impact, EVs offer a compelling alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. However, the widespread adoption of EVs hinges on the development of a robust and accessible charging infrastructure. Electric vehicle charging stations play a crucial role in this regard, providing convenient and reliable means for EV owners to replenish their vehicles’ batteries.
This essay delves into the world of electric vehicle charging stations, exploring the different types, components, standards, and factors to consider when choosing a charging station. We’ll also examine the benefits of installing a home charging station, the availability and usage of public charging stations, and the future of EV charging infrastructure.

II. Types of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
Electric vehicle charging stations come in three main levels, each offering varying charging speeds and applications:
-
Level 1 charging: The slowest type of charging, typically used for overnight or home charging. It utilizes a standard household outlet (120 volts) and can add about 5 miles of range per hour of charging.
-
Level 2 charging: Faster than Level 1 charging, commonly found in public places like workplaces and parking garages. It operates at 240 volts and can add about 25 miles of range per hour of charging.
-
Level 3 charging (DC fast charging): The fastest type of charging, primarily used for quick top-ups along highways. It delivers direct current (DC) power at high voltages (up to 400 volts) and can add about 100 miles of range in 30 minutes of charging.
III. Components of an Electric Vehicle Charging Station
An electric vehicle charging station consists of several key components that work together to provide a safe and efficient charging experience:
-
Power source: The electrical connection that provides the power to charge the EV. It can be a home outlet, a dedicated circuit, or a public charging network connection.
-
Charging cable: The cord that connects the charging station to the EV. It is typically insulated and designed to handle the high currents involved in charging.
-
Charging connector: The interface that physically connects the charging cable to the EV. There are various connector types, such as J1772, CHAdeMO, and CCS Combo 1.
-
Control panel: The user interface that allows users to monitor and manage the charging process. It may display information like charging time, energy consumption, and charging costs.
IV. Charging Standards and Protocols
To ensure compatibility and safety, electric vehicle charging stations adhere to established standards and protocols:
-
SAE J1772: The standard for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging in North America. It defines the connector type, electrical specifications, and communication protocols.
-
CHAdeMO: The standard for DC fast charging in Japan and some other countries. It utilizes a unique connector type and supports high-power charging.
-
CCS Combo 1: The standard for DC fast charging in Europe and North America. It combines the J1772 connector with DC fast charging capabilities.
-
Tesla Supercharger: A proprietary charging network and protocol developed by Tesla. It offers high-power charging exclusively for Tesla vehicles.

V. Factors to Consider When Choosing an Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Selecting the right electric vehicle charging station depends on several factors:
-
Charging level: Consider the desired charging speed based on your driving habits and access to public charging. Level 2 is suitable for most daily needs, while Level 3 is ideal for long-distance trips.
-
Connector type: Ensure the charging station’s connector type matches your EV’s charging port. J1772 is common in North America, while CHAdeMO and CCS Combo 1 are prevalent in other regions.
-
Cost: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing the charging station varies depending on the type, power output, and installation complexity.
-
Features: Additional features like payment options, remote monitoring, and load balancing can enhance the charging experience and optimize energy usage.
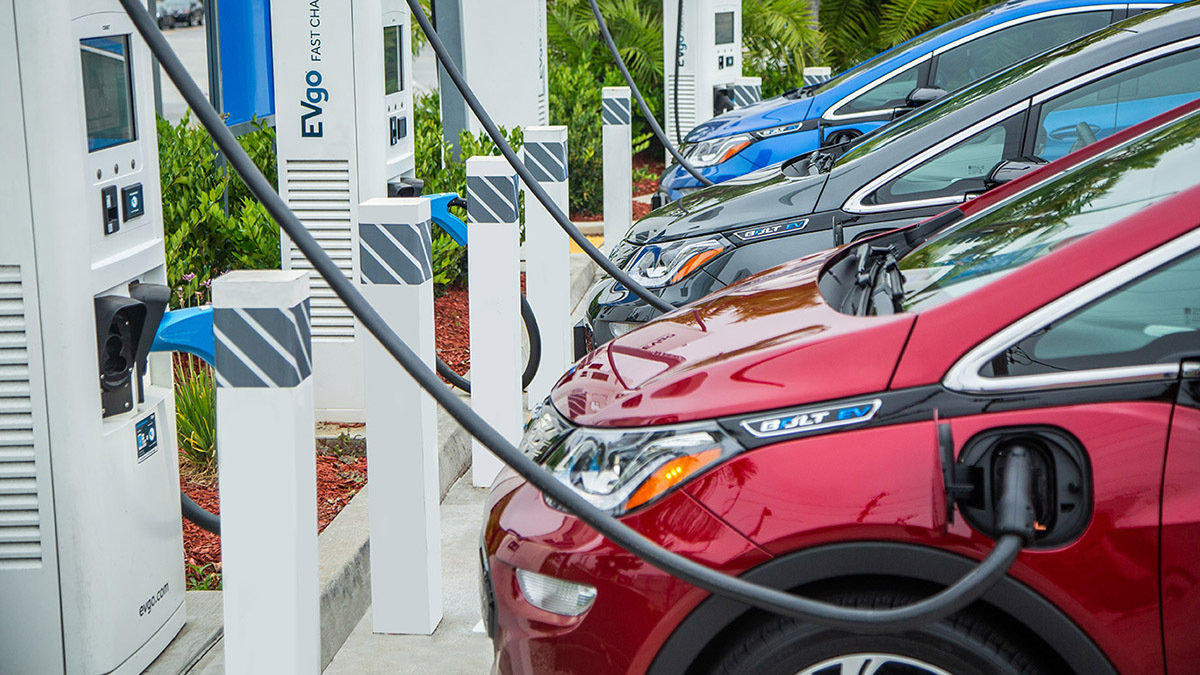

VI. Benefits of Installing an Electric Vehicle Charging Station at Home
Owning a home electric vehicle charging station offers several advantages:
-
Convenience: Charge your EV at home overnight or whenever it’s parked, eliminating the need to seek out public charging stations.
-
Cost savings: Electricity costs are typically lower than gasoline or diesel, leading to significant savings over time.
-
Environmental impact: Reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to cleaner air quality by using renewable energy sources to charge your EV.
-
Increased property value: Homes with EV charging stations are often seen as more desirable and can potentially command higher resale values.

VII. Public Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
The availability of public charging stations is crucial for long-distance travel and for those who lack access to home charging. Public charging stations are becoming increasingly widespread, popping up in various locations:
-
Retail centers: Shopping malls, grocery stores, and other retail locations often provide public charging stations as a convenience for customers.
-
Workplaces: Many employers are installing charging stations on their premises to encourage employee adoption of EVs and promote sustainability.
-
Parking garages and lots: Public parking garages and lots are increasingly incorporating charging stations to cater to a growing demand.
-
Hotels and resorts: Hospitality businesses are recognizing the need for charging options and are offering charging stations for guests with EVs.
-
Rest stops and travel plazas: Charging stations along highways and major roadways are essential for long-distance travel with EVs.
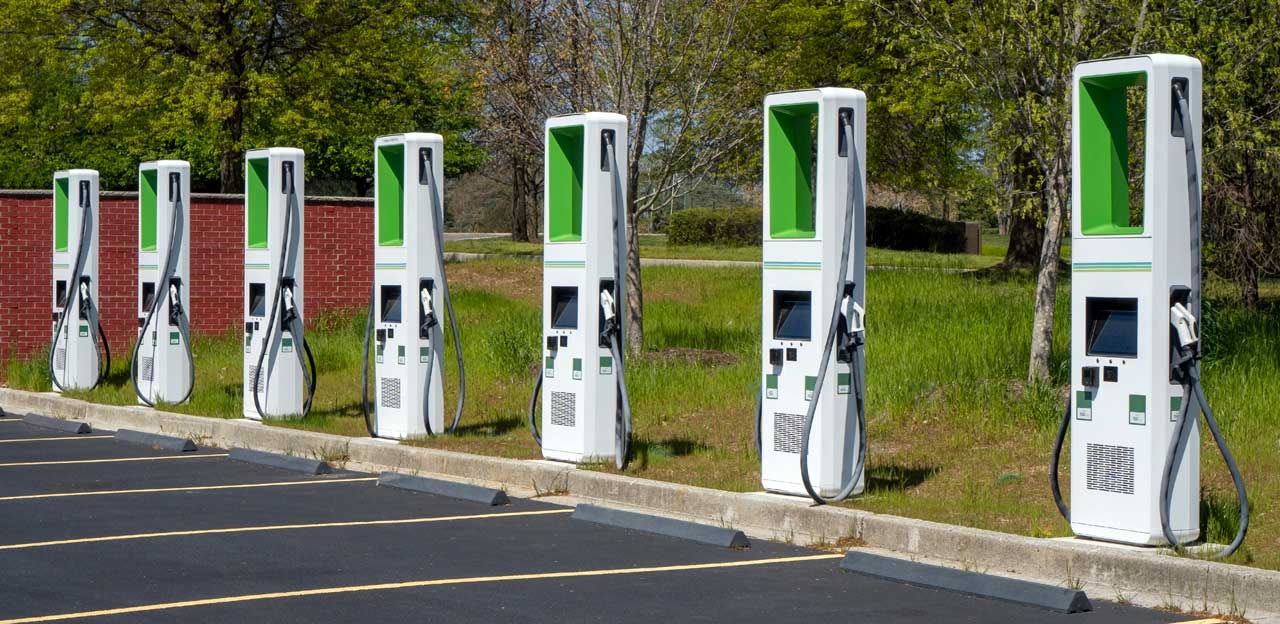

The types of public charging stations mirror those available for home use – Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging. However, using public stations involves additional considerations:
-
Charging fees: Public charging stations often have associated fees which can vary depending on the location, provider, and charging speed (DC fast charging typically costs more).
-
Payment methods: Various payment methods are used at public stations, including credit cards, mobile apps specific to charging networks, and membership programs that offer discounts.
-
Station availability and usage: With the growing number of EVs, public charging stations can become occupied. Apps can help locate stations and check availability in real-time.
VIII. The Future of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure
As EV adoption accelerates, the demand for a robust and efficient charging infrastructure will continue to grow. Several key trends are shaping the future of EV charging:
-
Increasing demand for EV charging stations: Governments, businesses, and utilities are investing heavily in expanding the public charging network to meet the anticipated surge in EVs.
-
Smart charging technologies: Integrating charging stations with smart grid technologies can optimize charging efficiency and reduce strain on the power grid. Smart charging can prioritize charging during off-peak hours when electricity demand is lower.
-
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology: This technology allows EVs to feed power back into the grid, helping to balance supply and demand. V2G can potentially create a more stable and resilient electricity system.
-
Government incentives and policies: Many governments offer financial incentives for installing home charging stations and for businesses to build public charging infrastructure. Additionally, policies promoting renewable energy sources can further enhance the sustainability benefits of EVs.
IX. Conclusion
Electric vehicle charging stations are the backbone of the EV revolution. Their widespread availability and continued development will be instrumental in achieving a sustainable transportation future. This essay has explored the various types, components, and considerations related to electric vehicle charging stations. By understanding these factors, both potential EV owners and those involved in building the charging infrastructure can make informed decisions. As charging infrastructure evolves, with advancements in technology and increasing government support, the future of electric mobility appears bright. With convenient and reliable charging options readily available, EVs can truly become a mainstream transportation choice, leading to cleaner air, reduced emissions, and a more sustainable planet.


